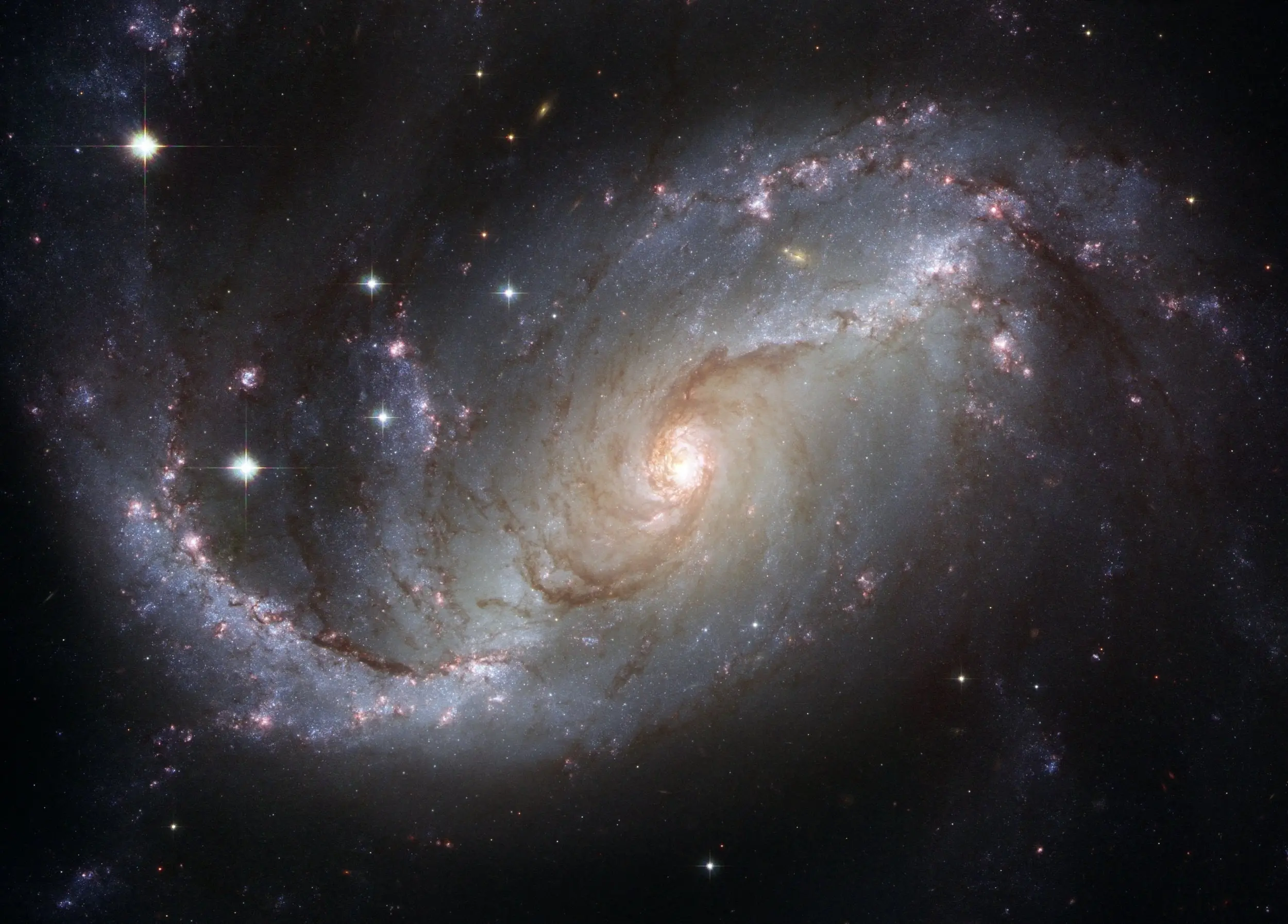
A low-spinning protogalactic cloud collapses into an elliptical galaxy due to its conditions. For instance, such a protogalactic cloud is usually dense, which allows it to cool to form stars before disk collapse, and this results in an elliptical galaxy (Galaxies [PowerPoint Slides]). A low-spinning protogalactic cloud has little or no initial angular momentum. Its high gas density leads to quicker cooling, which is linked to faster star formation before settling gas into a disk; thereby, resulting in an elliptical galaxy. A low-spinning protogalactic cloud does not stay so if there is very minimal spin because such a spin is associated with a change in its conditions, specifically, density changes. Any change in density contributes to the collapse of a protogalactic cloud, as gas collected in it starts cooling.
If our galaxy were to collide with another, life on earth would not cease to exist. Instead, the collision of the galaxies would lead to forming a new galaxy (Drake, 2014; Galaxies [PowerPoint Slides]). However, the earth would not be entirely unaffected, as collisions of galaxies will make it change its orbit. In a case of a collision between the two galaxies, gravity will make the sun move to a new orbit and drag other planets with it. Cases of galaxy collisions in the past have seen the formation of new galaxies, and no stars have directly hit each other (Drake, 2014). Therefore, the collision of our galaxy with another will not make life on earth cease to exist; instead, the earth will move to a new galaxy that will be formed due to the collision.
References
Drake, N. (2014). Milky way has 4 billion years to live-but our sun will survive. National Geographic. https://www.nationalgeographic.com/science/article/scientists-predict-our-galaxys-death
Galaxies [PowerPoint slides].