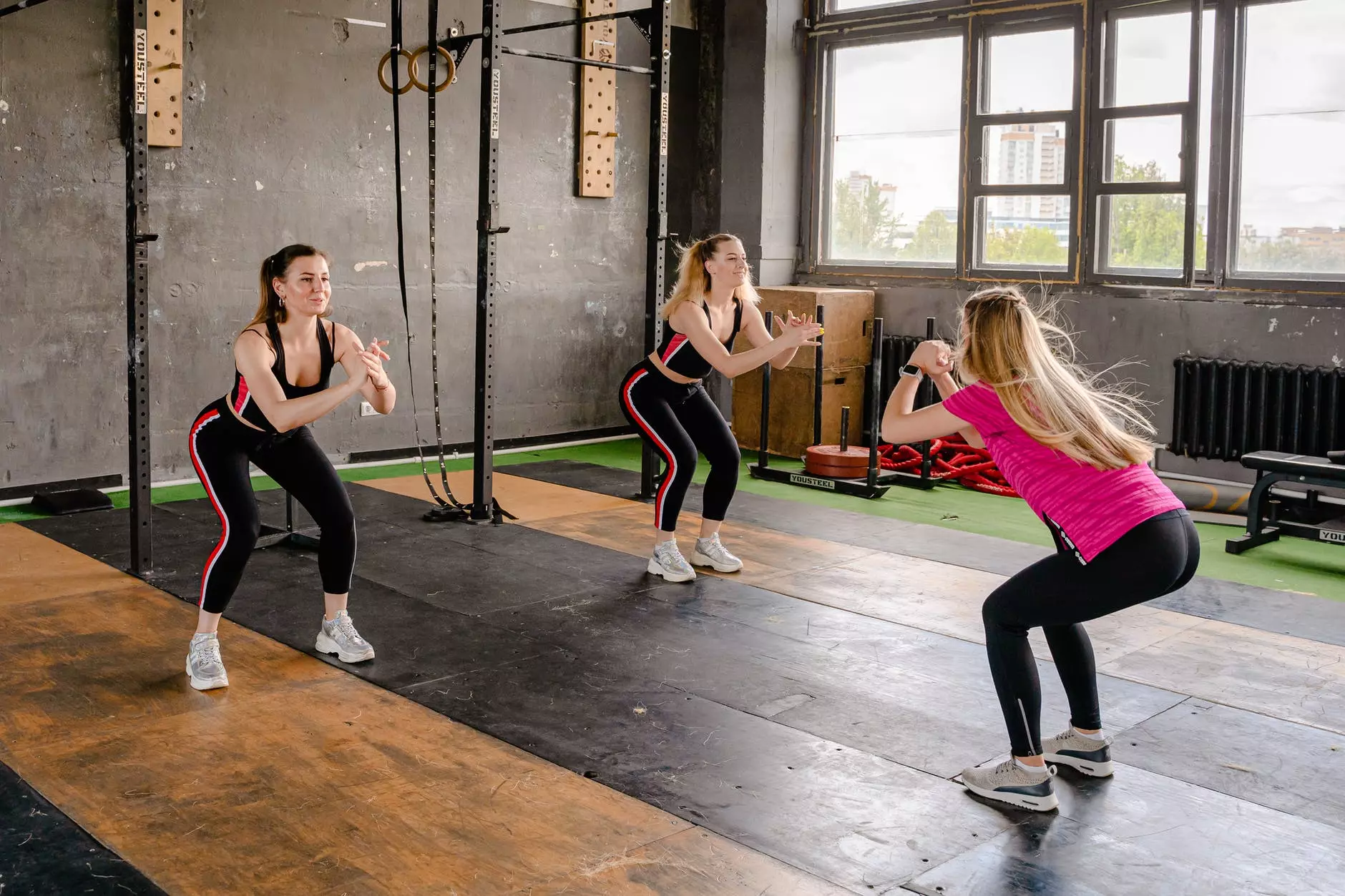Resistance training involves exercises that require moving or contracting our muscles against a form of resistance such as exercise equipment, gravity, or even our own weight. Examples are weightlifting, pull-downs, push-ups, chin-ups, squats, lunges, planking, crunches, leg raises, and donkey kicks.
Under normal conditions, our tendons and muscles react differently depending on the resistance and amount of force exerted to counter it. This is called a muscle contraction and it occurs in three phases: isometric, concentric, and eccentric contractions. In an isometric contraction, our muscles remain static and force does not change the muscle length, typically while holding a position for a certain period, such as in yoga poses or planks.
Concentric and eccentric contractions occur when performing isotonic exercises where muscles extends or shortens depending on the movement and amount of force required to counter the resistance on the muscle. During a concentric contraction, the length of the muscle shortens and its angle to the joint it is attached to changes. Notice our biceps muscle visibly bunch as it shortens when lifting a heavy weight upwards. Conversely, an eccentric contraction is when the muscle lengthens in response to the lifted weight being lowered. The muscle in this phase is at its strongest as it tries to maintain control of the load when lowering the weight while the muscle stretches at the same time.
Being able to combine all three phases efficiently can create a more focused workout plan. One that is specific to each body need and target goal, whether it is bulking up, strengthening, or losing weight.
References
Anthony, K. (2018). What Are Concentric Contractions? Healthline. Retrieved from
https://www.healthline.com/health/concentric-contraction
OER Services. Types of Muscle Contractions: Isotonic and Isometric. Lifetime Fitness and
Wellness. Retrieved from https://courses.lumenlearning.com/suny-fitness/chapter/types-of-muscle-contractions-isotonic-and-isometric/
Accessed 02 August 2019
Weil, R. (2018). Resistance Training. eMedicine Health. Retrieved from
https://www.emedicinehealth.com/strength_training/article_em.htm#what_is_resistance_training